Grade 3 - Earth and Space Sciences
Vocabulary
An Ocean is a large body of salt water.
A continent a large area of land.
A Landform is a feature of land on the earth's surface.
Weathering is the breaking down of rocks into smaller pieces.
Erosion is the movement of weathered rock or soil by water or wind.
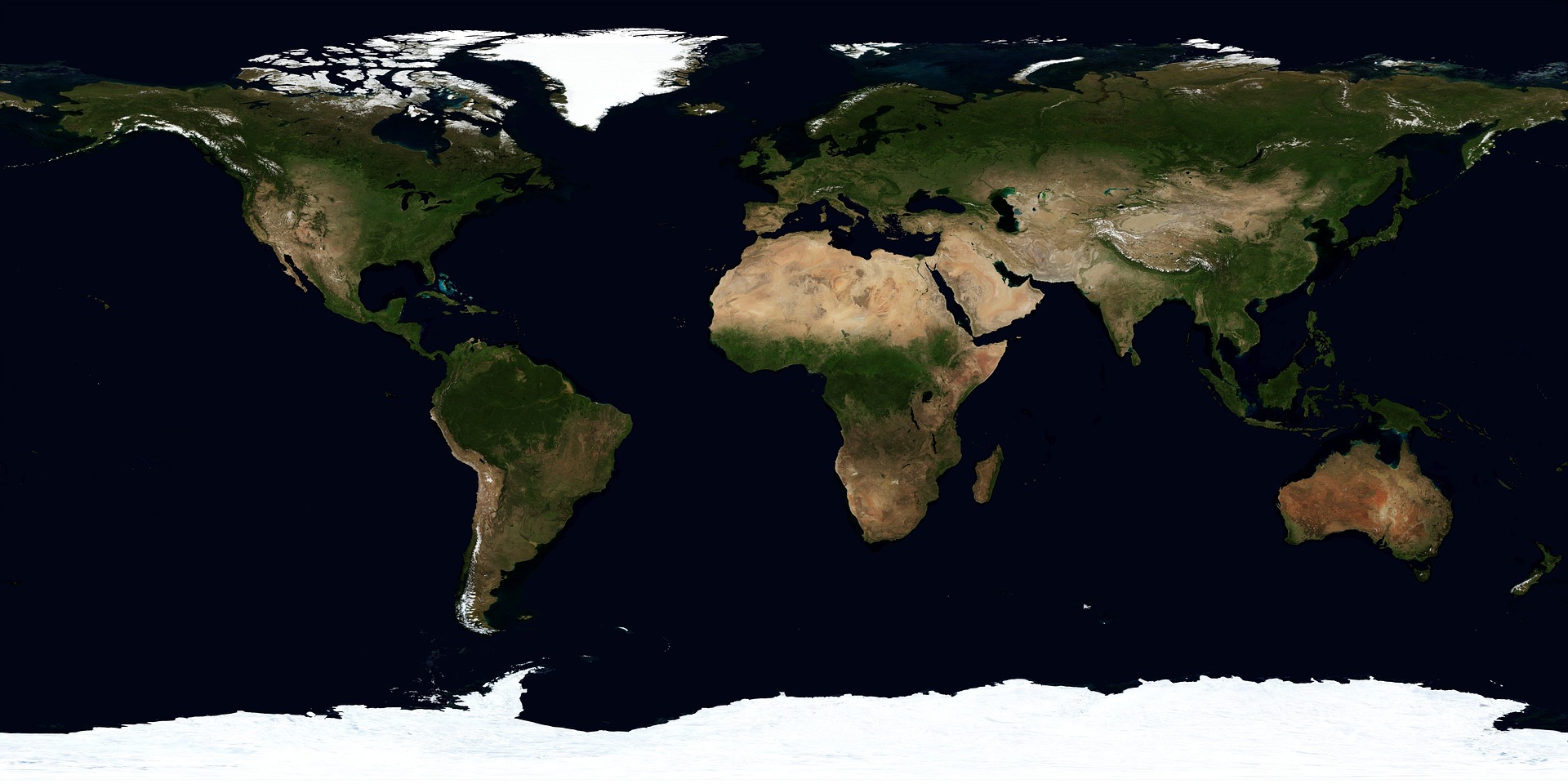
Lesson 1 a: Earth’s Features
Most of the earth is covered by water. Most of this water is in oceans. Rivers, lakes, ponds, streams, glaciers etc are other types of water bodies. Oceans are made up of salt water. Lakes may be salty or fresh water. Rivers, streams and ponds are made up of fresh water.
The earth also has seven great areas of land called continents. The map above shows the oceans and continents. Maps usually have a key that shows what a map’s colors and shapes mean.
There are many land and water features on Earth. Land features are called landforms.
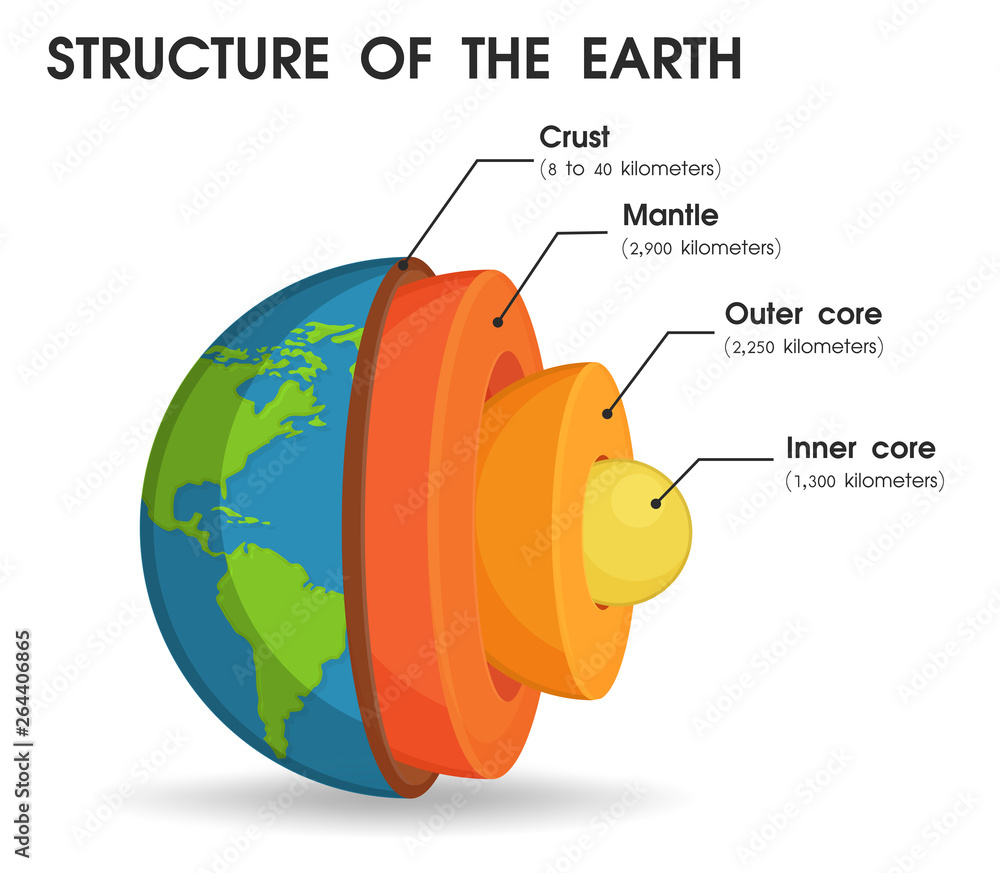
Lesson 1 b: Earth’s Layers
Like an egg, Earth has several layers. The continents and ocean floor make up Earth’s outermost layer, called the crust. The crust is Earth’s thinnest and coolest layer. The layer below the crust is the mantle. Part of the mantle is solid rock. Part is nearly melted rock that is soft and flows. It is a lot like putty. At the center of Earth is the core. The core is the deepest and hottest layer of Earth. The outer core is melted rock. The inner core is solid rock.
Lesson 2: Weathering and Erosion
The breaking down of rocks into smaller pieces is called weathering. Running water, wind, rain, and temperature changes are some things that break down rocks. Running water and wind pick up small rocks. These rocks scrape against other rocks. This scraping slowly wears away rocks.
Living things can cause weathering. Plants may grow in the cracks of rocks. Their roots eventually split rocks apart. When animals dig in the ground, they can uncover buried rocks. The uncovered rocks can then begin to weather.
Once rocks are weathered, they undergo erosion, that is they are moved to other places. Moving water, wind, and glaciers all cause erosion. A glacier is a mass of ice that moves slowly across the land. Gravity also causes erosion. Gravity can make weathered materials move downhill.


Lesson 1: Minerals and Rocks
A mineral is a solid, nonliving substance found in nature. Minerals are the building blocks of rocks.
There are more than 3000 kinds of minerals. Each mineral has its own properties.
Properties of Minerals
- Color: Most minerals have only one color. A few like Quartz have many colors.
- Streak: Streak is the color of the powder left when a mineral is rubbed across a white tile. A mineral's streak may or may not be the same as the same minerals color.
- Luster: This is how light bounces off a mineral. Some minerals are shiny like metal, others are dull.
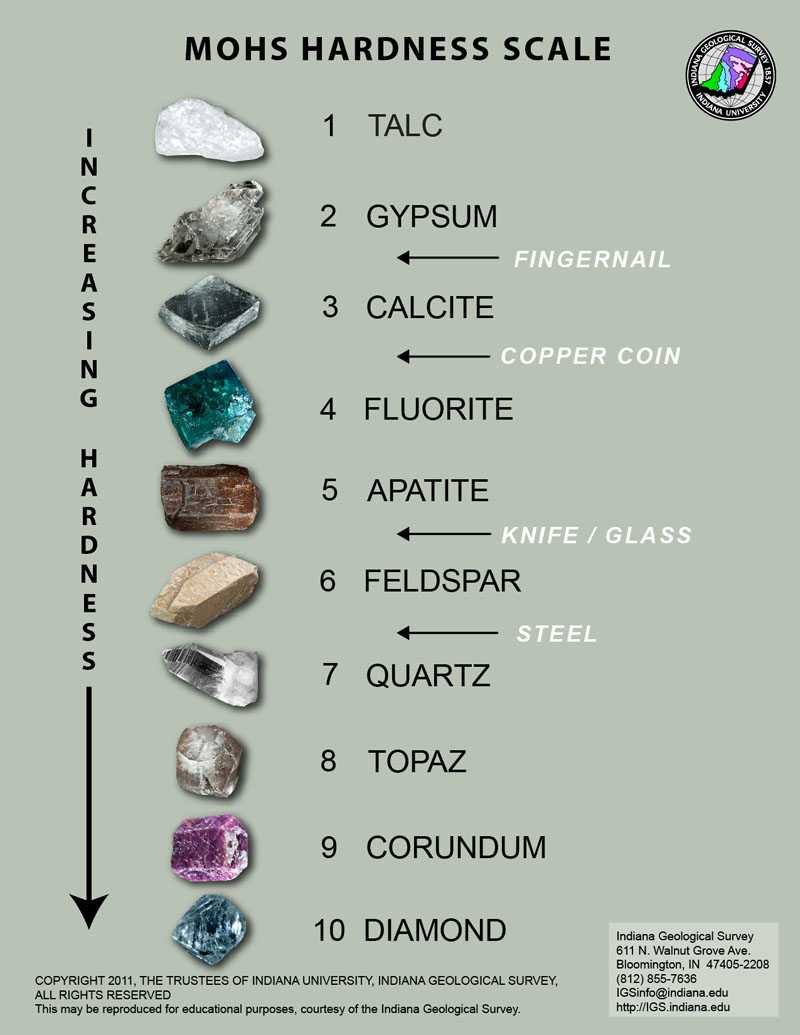
- Hardness: This is a measure of how easily a mineral can be scratched. Some minerals are soft and can be scratched with a fingernail. Others are hard and cant even be scratched by a metal.
Lesson 1b: Minerals and Rocks
A rock is a non-living material made of one or more minerals. There are several types of rocks. SOme rocks are made of many minerals while others are made predomrinantly by one mineral.
Rocks are made of grains that give the rock its texture. Some rocks have large grains that can be seen easily with just the eyes. Such rocks end up having a rough/coarse texture. Other rocks have fine grains and as a result have a fine/smooth texture.
There are three main kinds of rocks.
- Igneous rocks form when melted rock cools and becomes hard. The molten hot rock inside the earth is called Magma. When this magma flows onto the surface of the earth it is called lava. Lava cools and hardens quickly and results in a rock with smooth grains. When magma cools slowly below the earth surface, it forms granite, which has a corse texture.
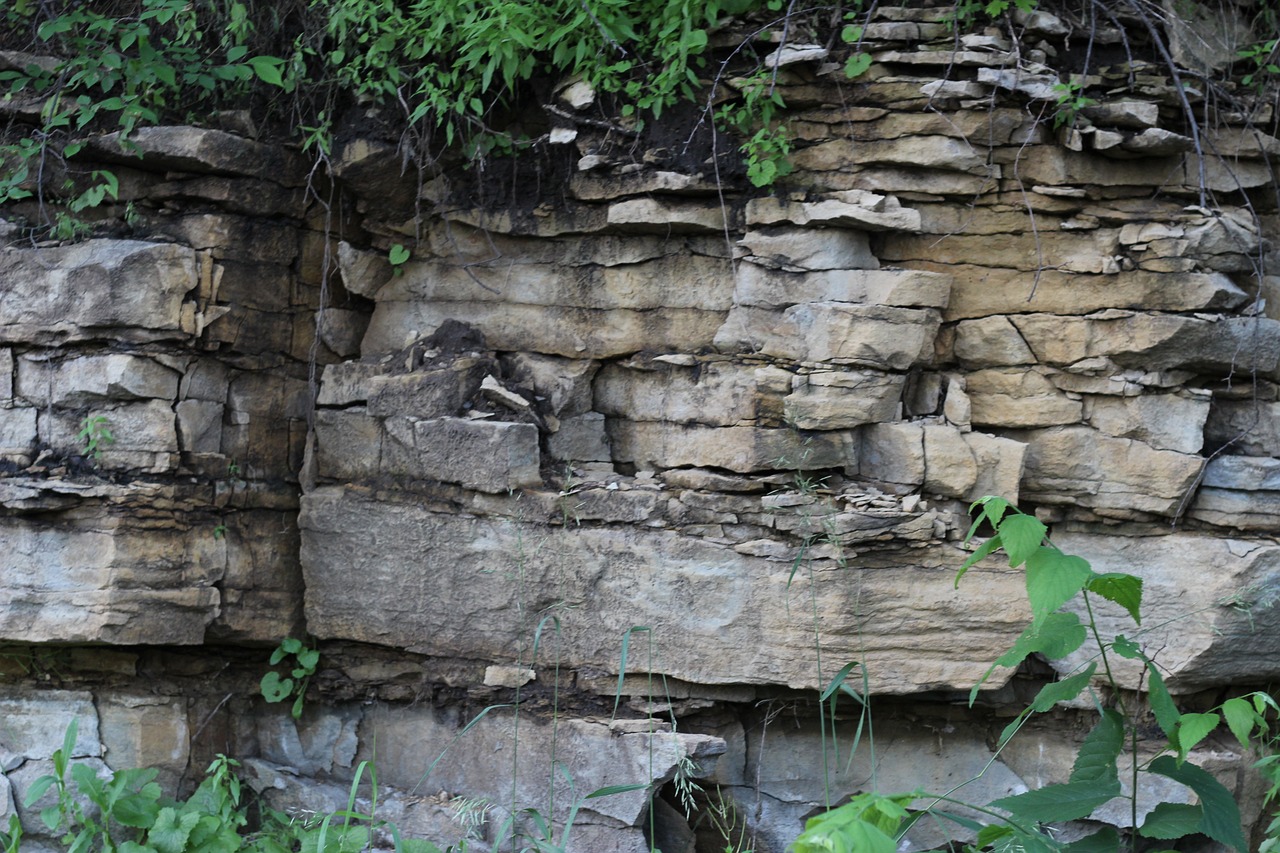
- Sedimentary rocks form by sediments of weathered rock or fossils. Sandstone, limestone and shale are examples of sedimentary rocks.
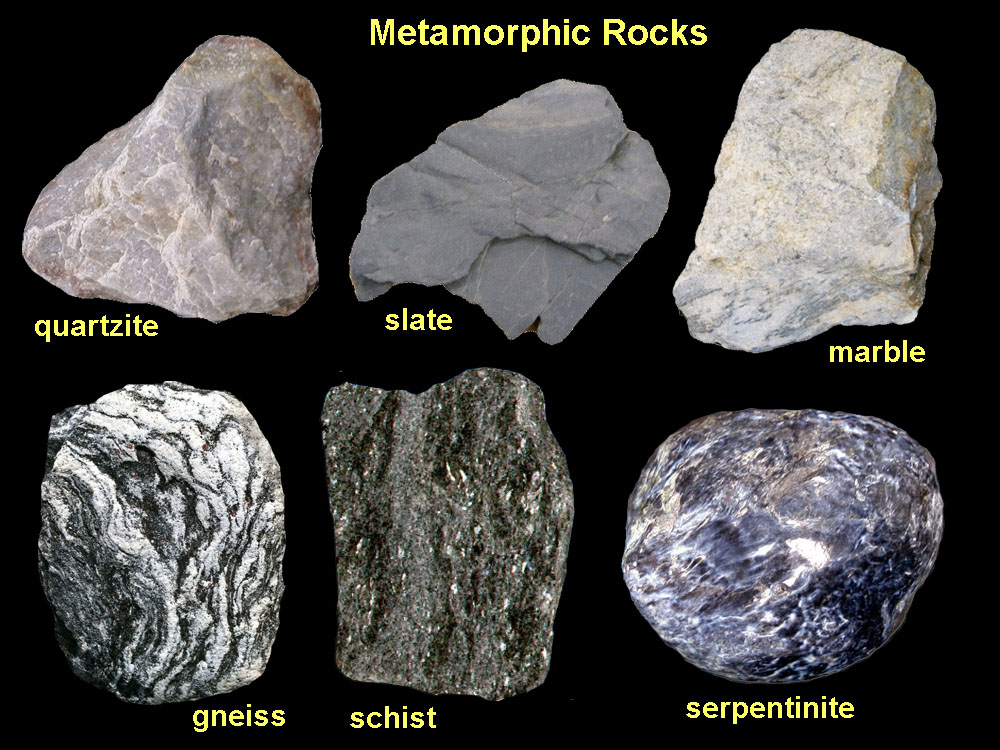
- Metamorphic rocks are rocks that have changed by heating and squeezing. Deep inside the earth, the heat and pressure/weight from other rocks creates the heating and squeezing needed to create metamorphic rocks. A new rock forms with properties that are different from the original rock.
Rocks and minerals have multiple uses from building houses, making jewelry and other even more common uses. The mineral graphite is used to make pencil points. Aluminum is used in cooking pans, and electric wires. copper is used in making coins, electric wires and water pipes. Calcium, a mineral which is found in milk, is essential for bone development. It is also predorminant in limestone and may be used to make chalk.



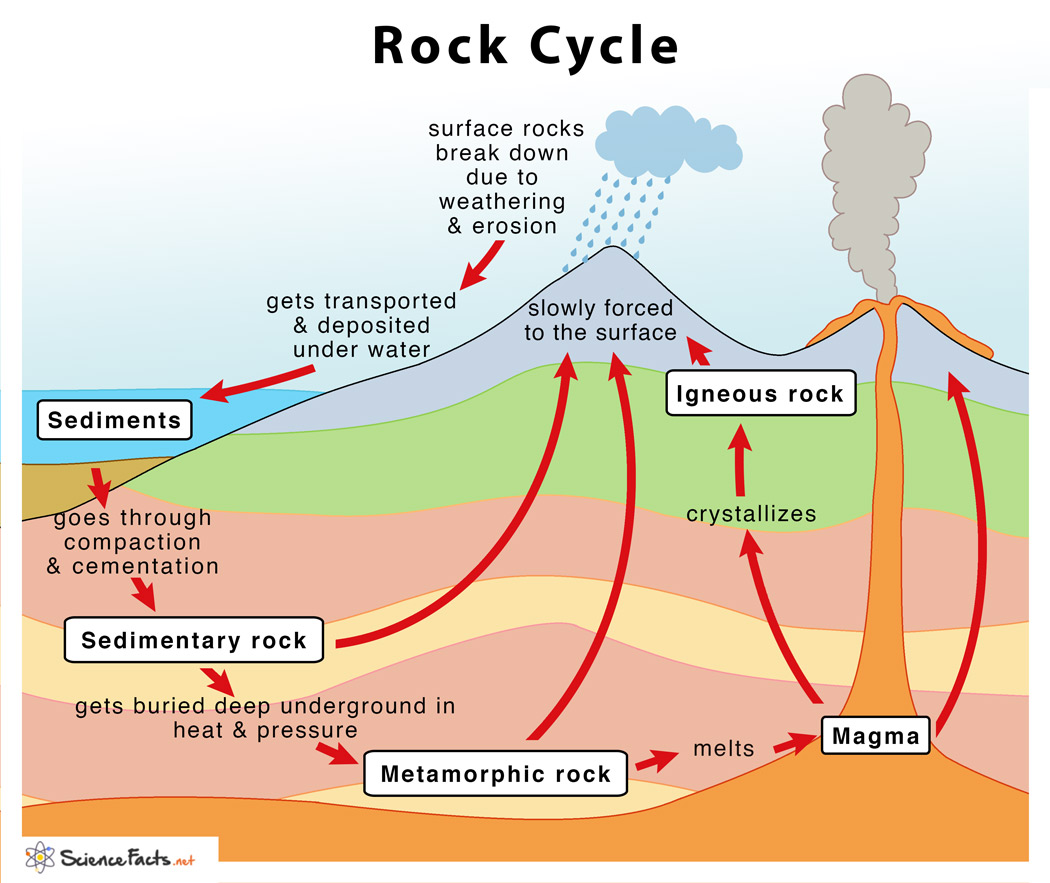
Lesson 1c: The Rock Cycle
The rock cycle is the process that describes the gradual transformation between the three main types of rocks: sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous. It is occurring continuously in nature through geologic time.
Steps in the Rock Cycle:
- Formation of Igneous Rock – Melting, Cooling, and Crystallization.
- Formation of Sedimentary Rock – Weathering, Erosion, Sedimentation, and Compaction.
- Formation of Metamorphic Rocks – Metamorphism.
- Weathering.
- Transportation.
- Deposition.
Lesson 2a: Soil
Soil is a mixture of minerals, weathered rocks, and other things. It has bits of decayed plants and animals called humus
Humus is dark in color. It adds nutrients to soil. Plants use these nutrients for their growth. Humus works like a sponge to soak up rainwater and keep the soil moist. Water, air, and living things are also found in soil.
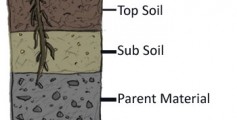
The making of soil starts with weathering. Weathering causes rocks to break down into smaller and smaller pieces. The tiny bits of weathered rock build up into layers.
The top layer is called topsoil. Topsoil is dark and has the most humus and minerals. Below the topsoil is subsoil. This layer is lighter in color and has less humus. Below the subsoil is bedrock, or solid rock.
Lesson 2b: Properties of Soil
Soil Color: The color of soil depends on the contents. Soil that has high amount of humus appears dark/black colored. Soil that is high in iron appears red. Soils with high calcite look whitish in color.
Soil Texture: Soil texture is a description of the pieces of grain that make up the soil. Sandy soil has larger grains and does not retain water. Silty soils have smaller grains than sandy soils. Clay soil has the smallest grain sizes. Loam soils is a mixture of sand, silt and clay.

Lesson 3: Fossils and Fuels
We have already reviewed fossils in our Life Sciences topic.
A fossil fuel is a fuel that forms from the remains of ancient plants and animals.
Oil is a fossil fuel found in rocks deep below Earth’s surface. People use huge drills to dig deep underground for oil. Pumps are used to bring oil to the surface.
Fossil fuels are natural resources. There are two types of natural resources: Renewable and non-renewable resources. Renewable resources are those that can be replaced and used again and again. such as water, animals, plants, air. Non-renewable resources are those that cannot be replaced or reused easily. Fossil fuels are non-renewable resources. Once they are harvested and used, they are lost forever.
Energy can be obtained from renewable resources such as the sunlght (solar energy), wind (wind power), moving water can be used to generate energy.


Contact Us
