Grade 2 - Life Sciences
Vocabulary
Flower is the part of the plant that makes seeds or fruit.
Seed is the part of the plant that can grow into a new plant.
Pollen is a sticky powder found inside a flower that helps make seeds.
Seedling is a young plant.
A mammal is an animal with hair or fur that feeds milk to its young.
An insect is an animal with six legs, and a hard outer shell.
Larva is a stage in the life cycle of some animals after they hatch from an egg.
Adaptation is the body part or the way an animal acts that helps it stay alive in an environment.

Seedlings
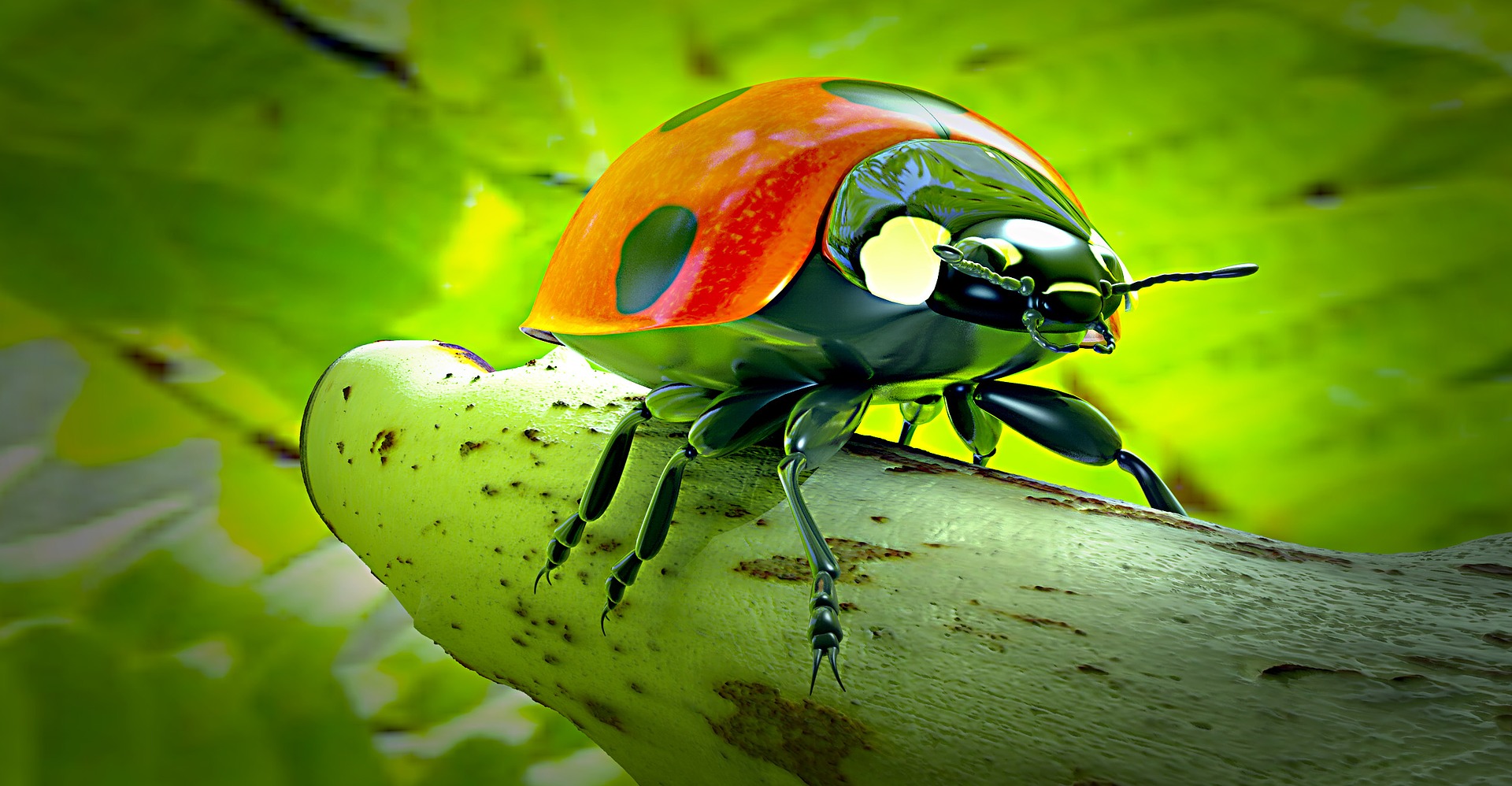

Insect (ladybug) see the 6 legs and hard shell.
Lesson 1: What Living Things Need
In Grade 1, you learnt that living things grow and change. Sometimes it is easy to tell when something is living. For example, you can see animals move, breathe air in and out, eat food, and drink water. It might be harder to tell in other cases, for example, some kinds of mushrooms found on dead and rotting tree trunks may not look like living things. We have to watch plants over a period of time to see them change (grow).
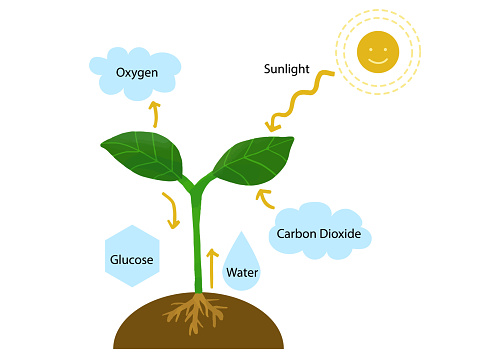
Like all living things, plants need air, water, and space to live and grow. They also need food. Plants make their own food.
Like you, plants also need minerals. Minerals are bits of rock and soil that help plants and animals grow.
When plants make food they release a gas called oxygen into the air. Oxygen is what humans and other animals breathe in order to live.
Lesson 2: Plants Make New Plants
The flower is the part of the plant that makes seeds and fruit. The seed is the part that can grow into a new plant. Seeds vary in size, appearance and in the way they can be used to produce new plants.
There is a part of the flower called Pollen. You might have heard about pollen allergy. Pollen is a sticky powder inside the flower that goes through a complex process ending with making seeds.
The pollen needs to be moved to different parts of the flower within the same plant, or from one part of the plant to another part of the same plant, or from one plant to another plant.
Most flowers also have a sweet sugary substance called nectar. Animals such as birds and bees visit flowers to eat nectar, but while feeding on nectar, the sticky pollen sticks on their wings and they can transport it to other flowers.
Wind and water can also help pollen move from one flower to another.
Seeds have many parts. All seeds have seed coats which protect the seed. Seed coats also help keep the seeds from drying out. Some seeds also have hard shells.
A life cycle shows how a living thing grows, lives, makes more of its own kind, and dies. The plant life cycle begins with a seed. Seeds need a warm place, light, water, and food in order to grow.
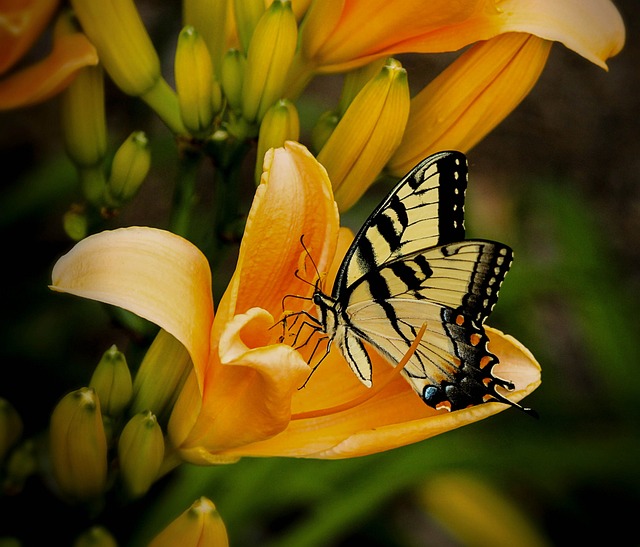
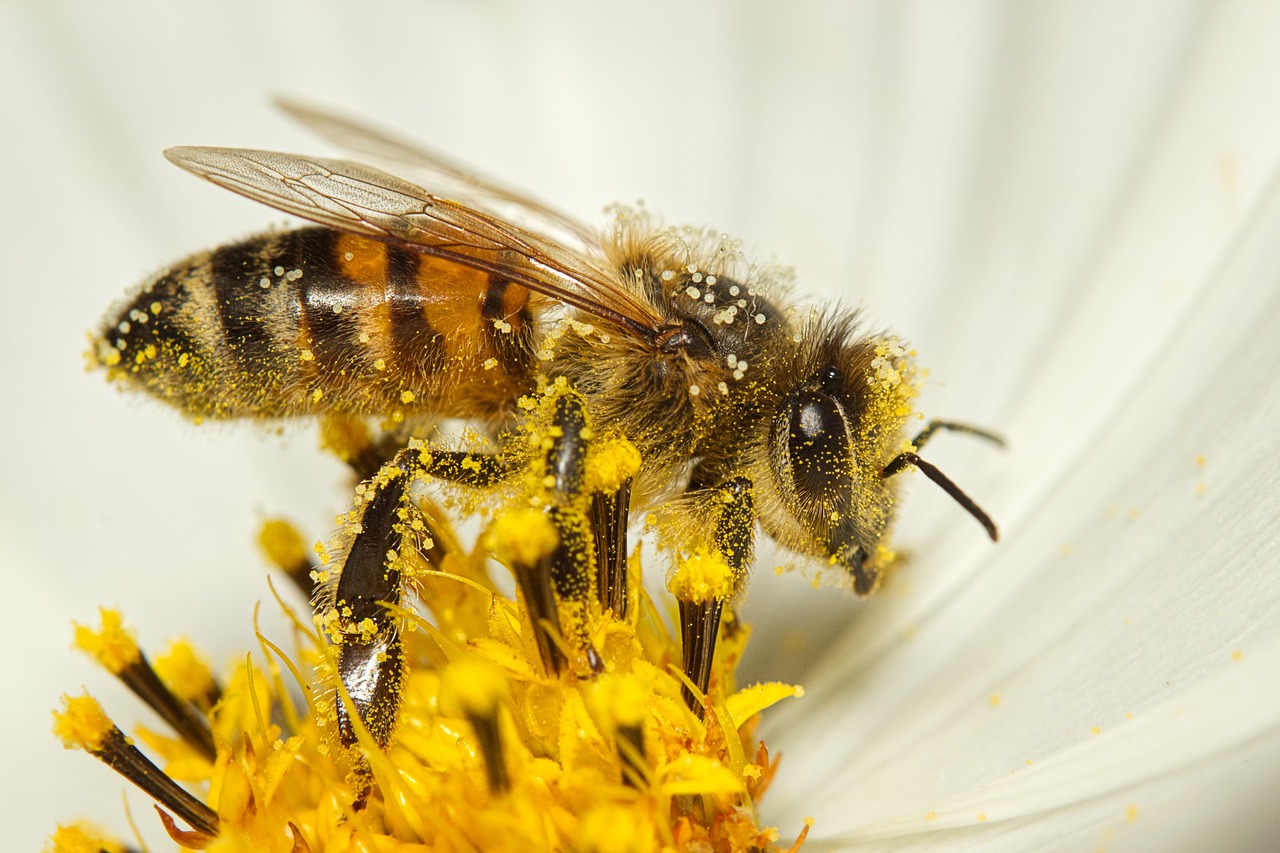



Lesson 3: How Plants Are Alike and Different
The properties / characteristics of an animal or plant are called traits. These properties are usually similar between the parent and their 'babies'.
Plants change to get what they need from the place where they live.
Cactus require little water to grow and they also lose less water so they grow best in the desert.
Palm trees grow tall and may be swayed by the wind so their stems can bend without breaking.
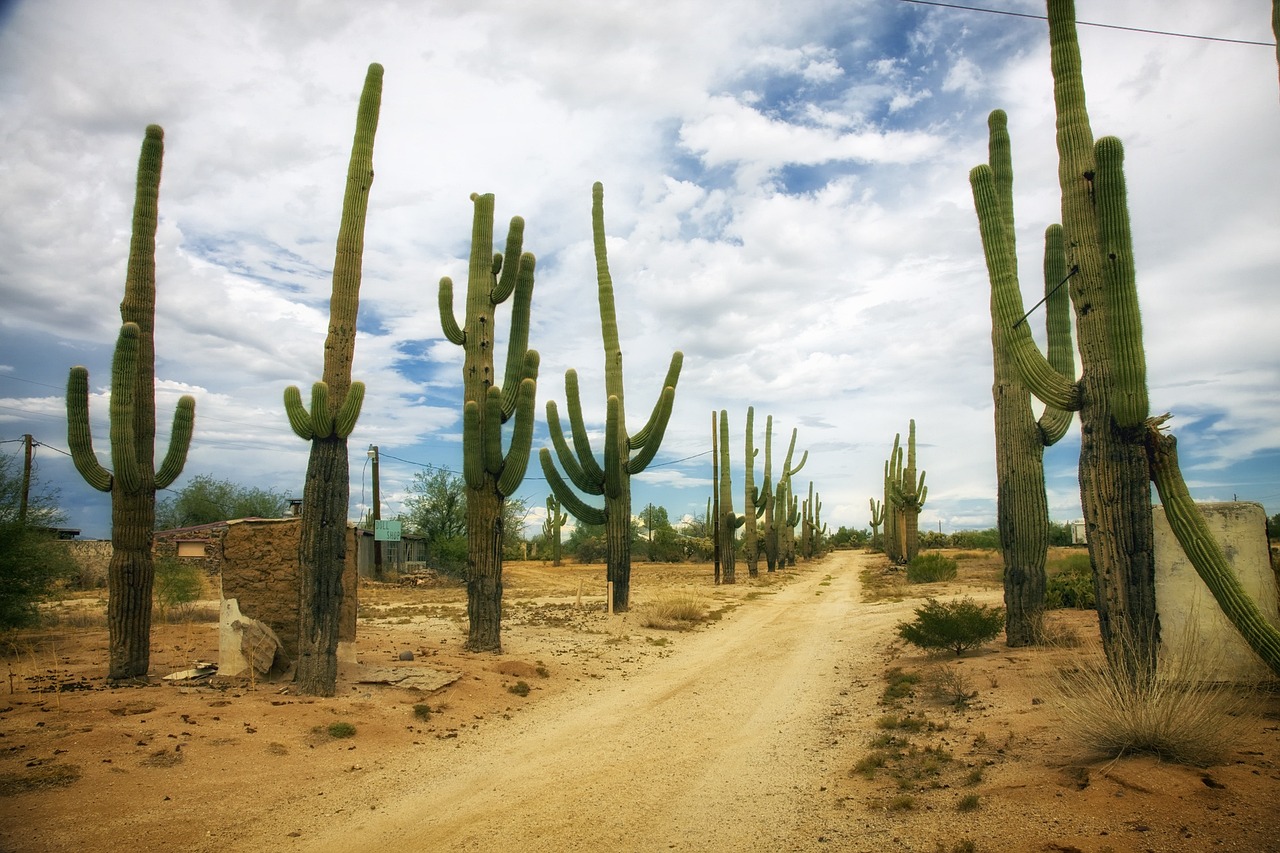


Lesson 1: Animal Groups
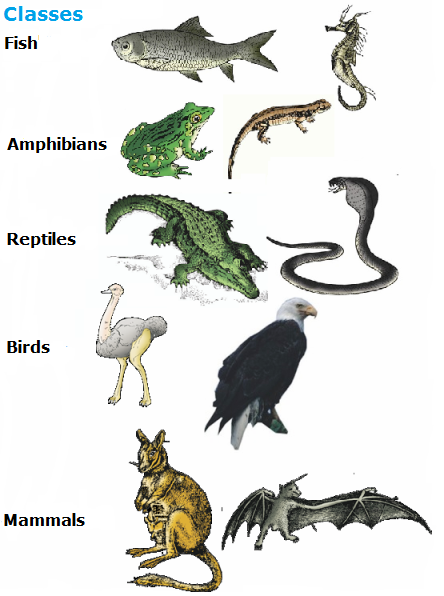
Animals can be classified into groups depending on their properties.
Animals with similar propoerties can be grouped together.
Animals in one group are different from animals in another group.
A mammal is an animal that has hair or fur. A female mammal makes milk for her babies. Mammals breathe through their lungs.
Birds are the only animals with feathers. All birds have two wings and a beak to help them get food. They lay eggs to hatch their young.
Reptiles (such as alligators, crocodiles and snakes) have a rough scaly skin for protection.
Amphibians (such as frogs and salamanders) can live in water and on land.
Insects are animals that have 6 legs (3 pairs) an antennae and a hard outer shell.

Lesson 2: Animals Grow and Change
Mammals give birth to live babies, which grow to maturity and the cycle repeats itself.
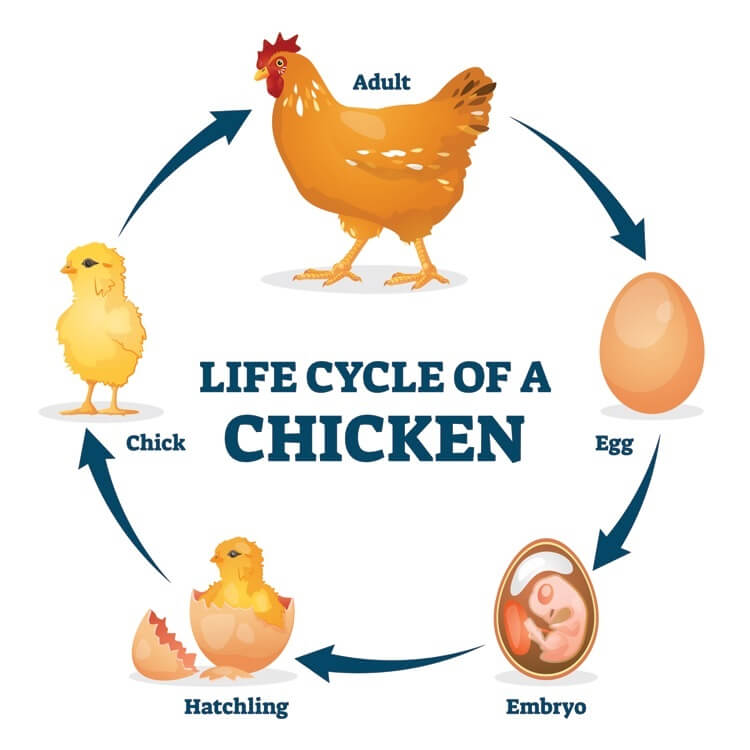
Chickens are birds and they lay eggs, which then hatch to produce a chick. The chick grows to maturity and produces new eggs. repeating the cycle. a male chicken is called a rooster, a female is called a hen. The hens are the ones that produce eggs.
All animals have a life cycle. A life cycle tells how an animal starts life, grows to be an adult, produces young ones, and dies.
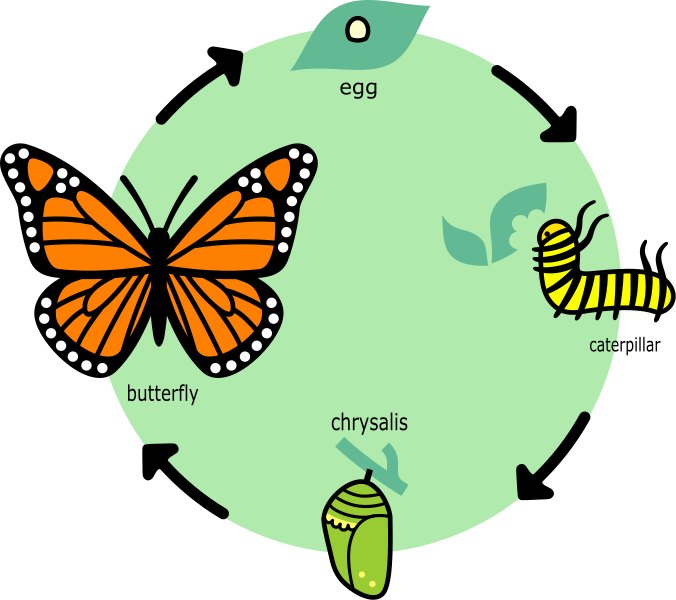
Other animals, such as butterflies, have more complex life cycles. The female butterfly lays eggs, the egg hatches into a caterpillar called the larva stage. catterpillars eat plants and grow. When the caterpillar is ready to change, it changes to a pupa. A butterfly pupa does not move, and its covered with a hard shell. Once the pupa has developed, the shell breaks open and the mature butterfly comes out.
Lesson 3: Staying Alive
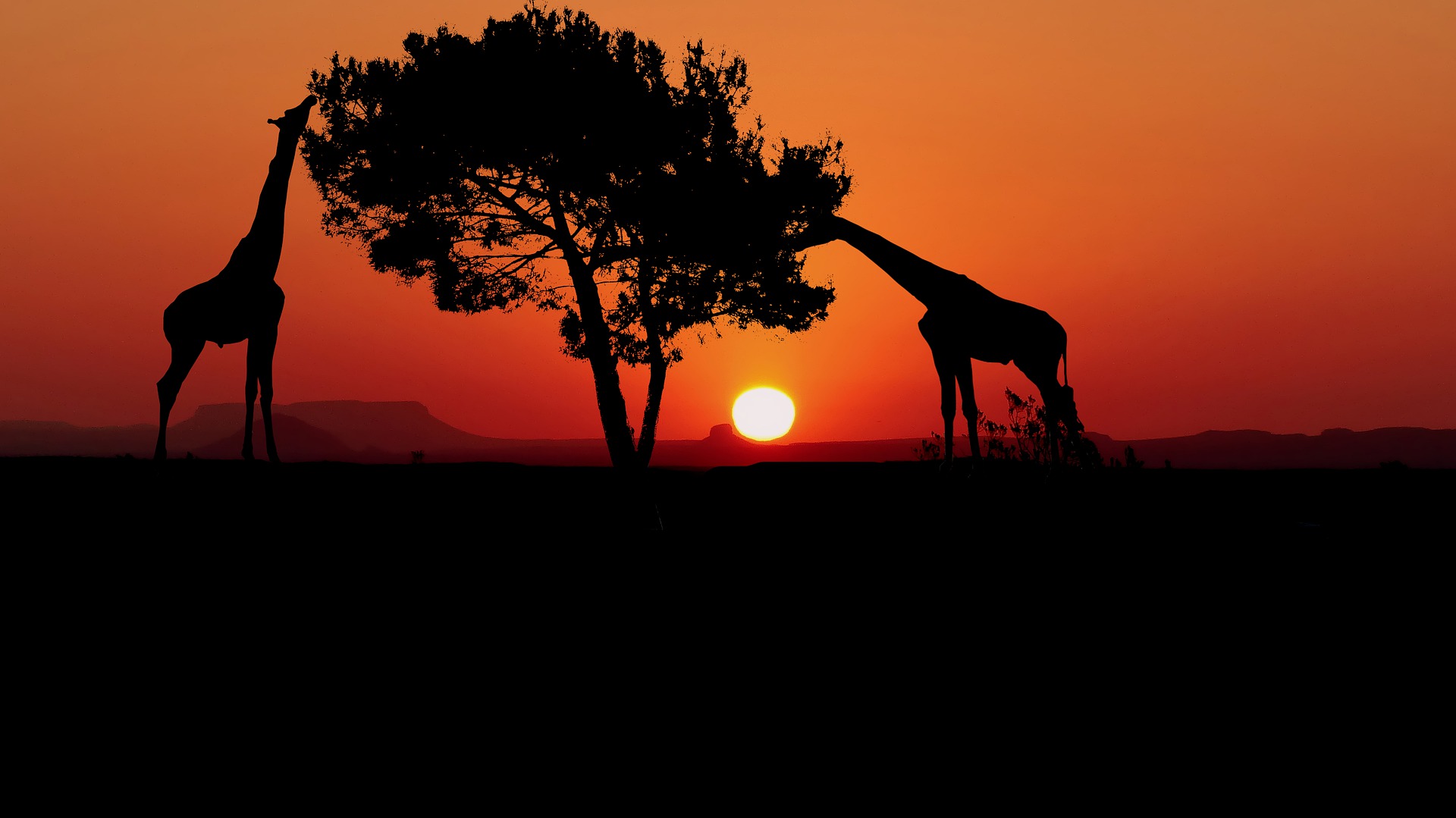
Animals have adaptations to help them stay alive. An adaptation is a body part or a way an animal acts that helps it stay alive.
Giraffes have long necks that help them reach leaves in the tops of trees.
Camouflage is a way that animals blend into their surroundings. The color or shape of an animal helps it hide. Camouflage keeps animals from being seen by their enemies.
Some animals, sleep during the cold winter.
Animals have body parts to keep them safe. Some animals have shells or release a smell to protect them from other animals. Skunks spray a bad smelling liquid to keep other animals away.


Lesson 1: Places to Live
A Habitat is a place where plants and animals live. Within the habitat, living things can find food, homes and water. Plants need soil, rain and sunlight in their habitat to stay alive.
There are many kids of habitats, some are dry, some get lots of rain, some are cold. Different plants can live in different habitats.
Animals use the plants living in their habitat for food. Some animals eat other animals that live in the same habitat. Animals also use their habitat to hide and sleep.
Various animals use different places in their habitat as their homes. Moles dig into the ground to make tunnels, while ants may make anthills.
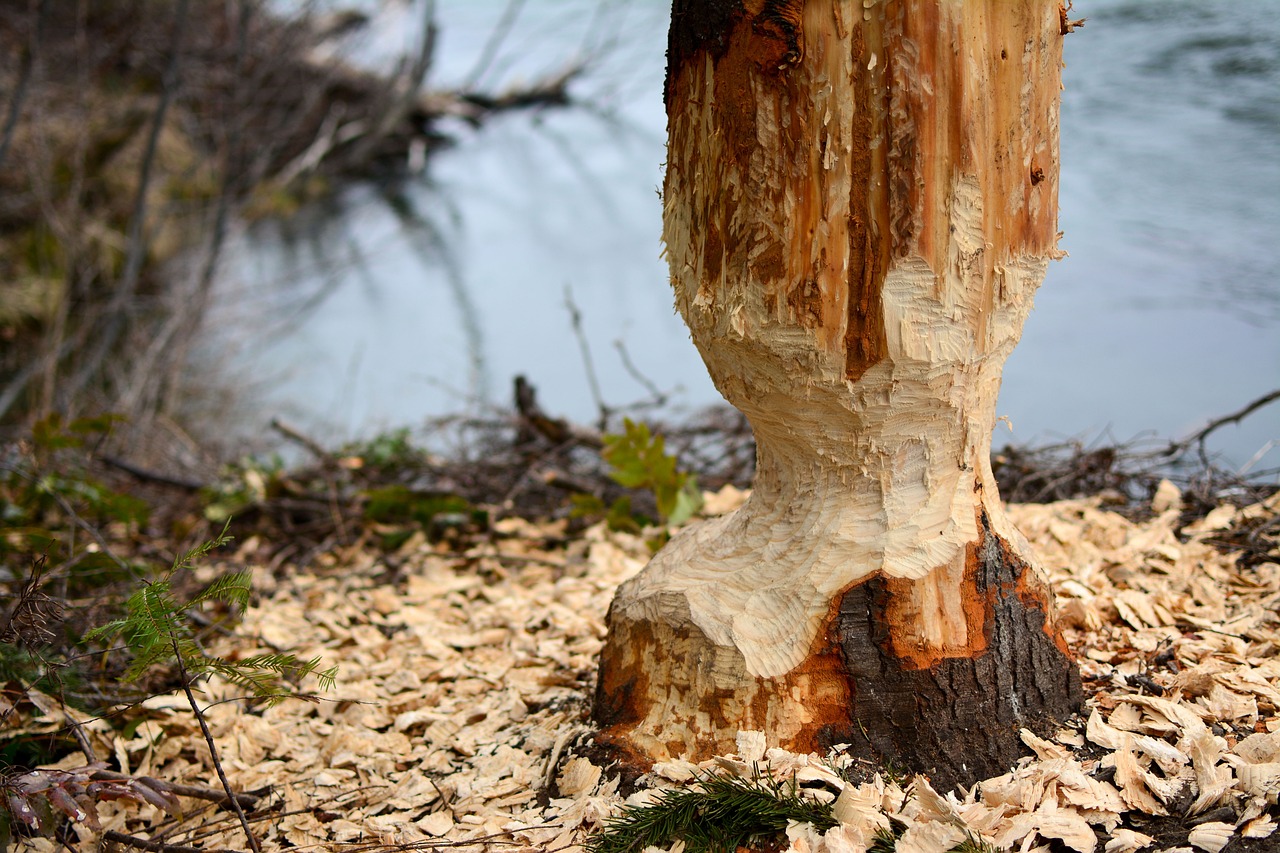
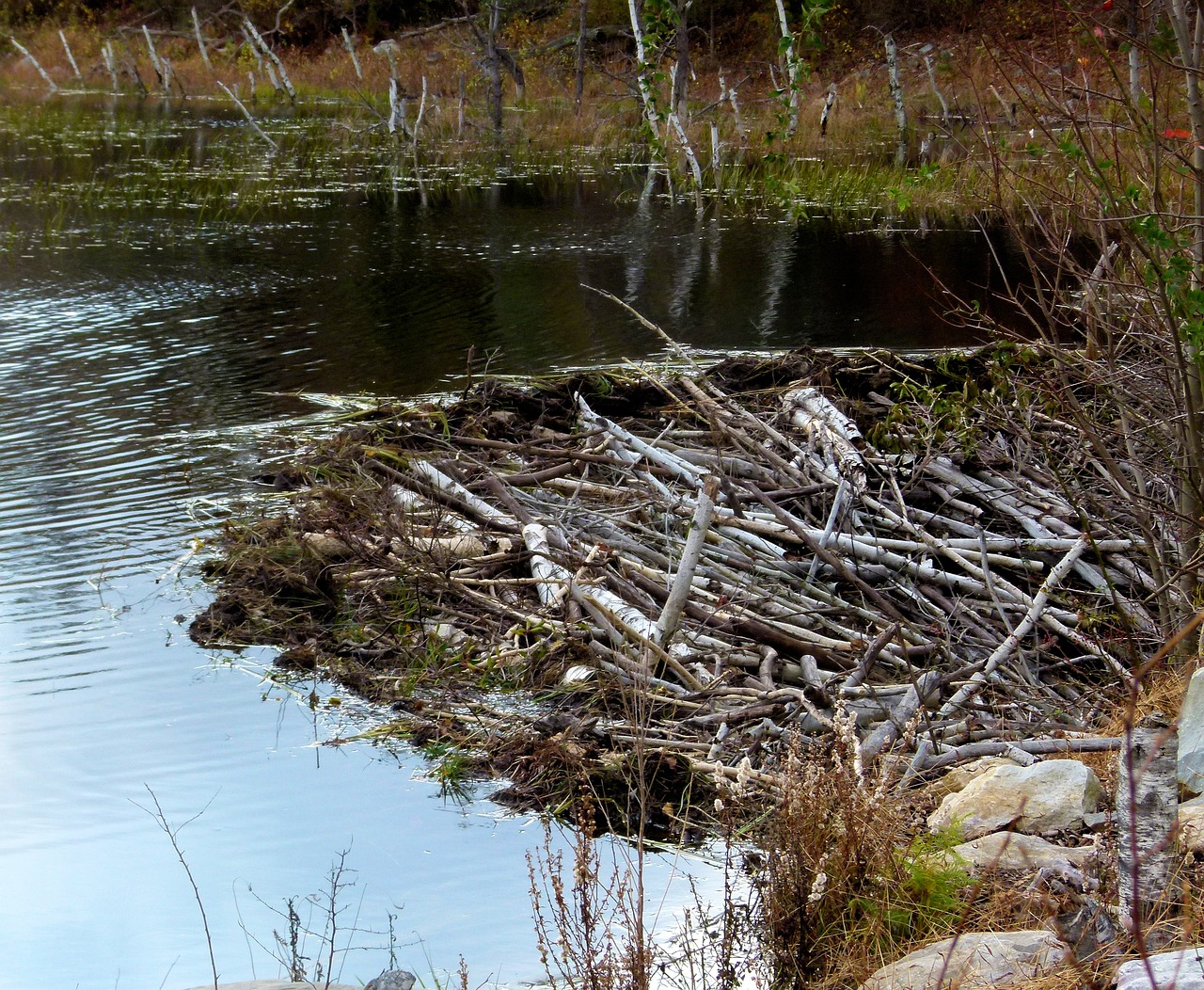



Lesson 2: Food Chains and Food Webs
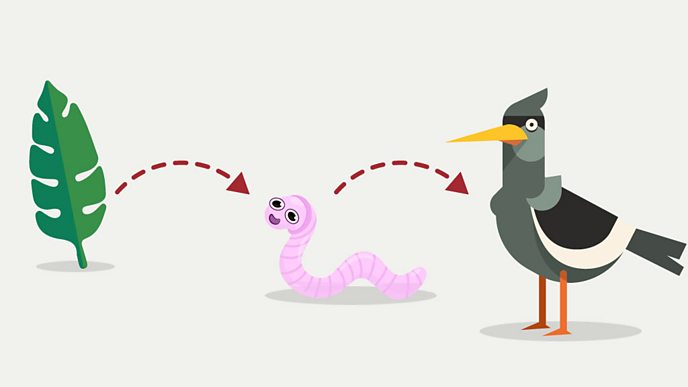
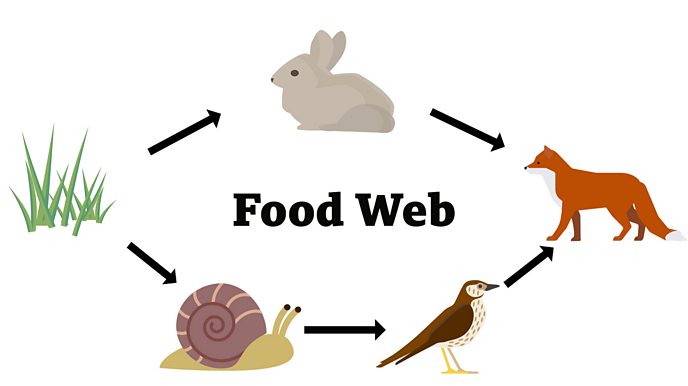
A food chain is a model of the order in which living things get the food they need. Most food chains start with the Sun.
An animal that hunts other animals for food is a predator. Animals that are hunted by predators are called prey.
Some animals eat plants and animals that are dead.
A food web is two or more food chains that are connected. Sometimes one kind of animal is food for many animals. Mice are eaten by hawks, owls, and snakes.
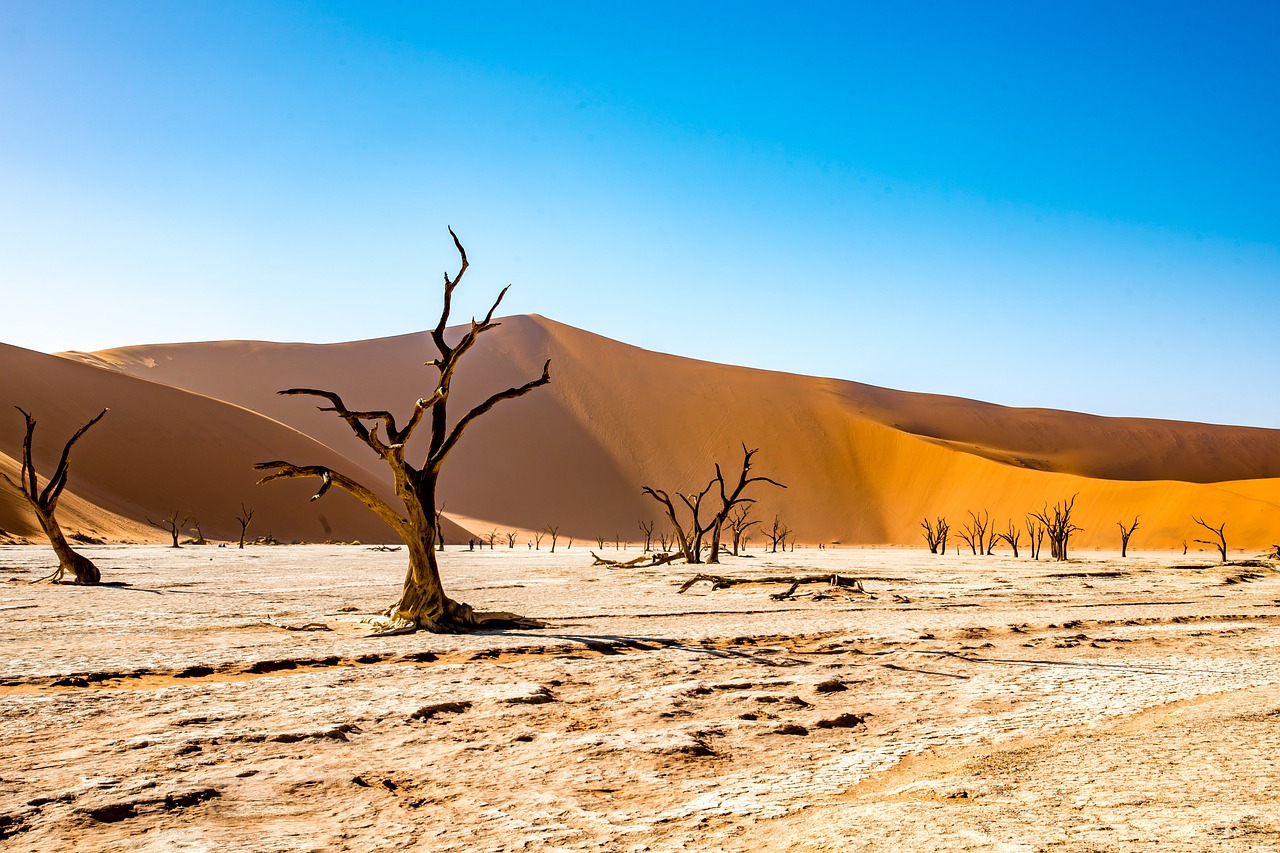
Lesson 3: Habitats Change
Nature can change habitats for example if a place expereinces a drought it cn change from being wet to being dry. A drought is a long period of time where there is little or no rain. Floods or fires can also change habitats.
People can change habitats too. For example, people can cut down forest trees to make lumber or to build houses.
When a habitat changes, animals may not be able to stay alive in the changed habitat. When many of one kind of animal die and only a few are left, that animal is endangered.
When habitats change, some animals have adaptations that help them live in their new habitat. Animals may find new places to get food and live.
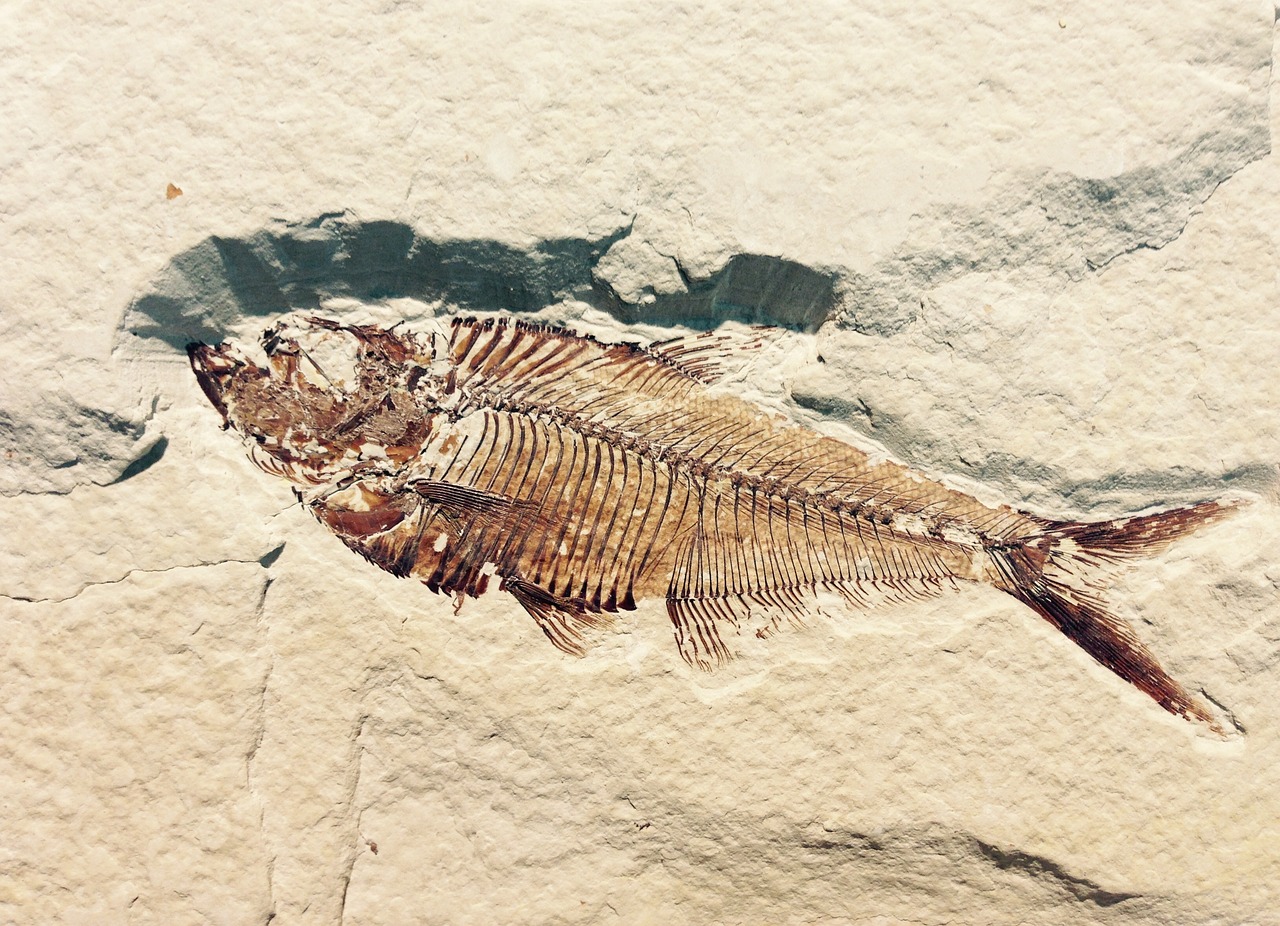
Scientists study fossils to learn about Earth’s past. A fossil is what is left of a living thing from the past.
Some plants and animals that lived long ago still live today. Some died out, or become extinct.


Contact Us
